Welcome 👋¶
KD4014, Programming with Python¶
Dr Lucy Whalley / l.whalley@northumbria.ac.uk.
ToDo: ¶
- Please sit in pairs
- Bookmark course website: lucydot.github.io/Python_Novice
- Complete questionnaire (link on course website)
Hello 👋¶
- ⚛️ Computational Materials Scientist: Theoretical Physics, Quantum Chemistry, Software Engineering
- 🌞 Renewable Energy materials: solar cells, batteries
- 💻 Software sustainability: writing code that lasts
Course outline¶
Part One: Getting started (Jupyter Notebooks)
Part Two: Python basics - data types, for loops, functions...
Part Three: Data arrays with Numpy
Part Four: Plotting with Matplotlib
Course resources¶
Website: lucydot.github.io/python_novice
Computer labs: Are important! Let me know if you cannot attend. Register will be kept. Will aim for 90 minute sessions.
Office hours: Tuesday 4-5pm.
Assessment¶
Coursework will be handed out 21st November, to be returned 20th December.
Must be done individually
Must be submitted as a Jupyter Notebook.
Why Programming? Computational Physics¶
Computational physics encompasses areas including materials modelling, particle physics simulations, protein structure prediction and plasma modelling. In fact, it is possible to find a computational branch for every major field in physics.

Why Programming? Employability¶
The focus of this course is to equip with you with some of the transferable skills needed for success in a range of computational disciplines, with examples tailored towards the physics domain.
Digital skills are no longer limited to tech and online roles, but are now nearly-universal requirements across all sectors and skill levels today (UK Government)
The demand for software developers is big, and it pays well – really well! (Just IT)
There's a lot of promise in quantum computing, but companies first need to figure out how they can attract more people into the industry. (Owen Hughes, Zdnet)

Why Python? The trade-off¶

Why Python? It gives you wings¶
Why Python?¶
- readable
- free to use
- cross-platform
- well documented
- widely used
Warning: Programming can be frustrating...¶

In programming, the little things matter! An extra full-stop or the smallest typo will stop your code running
...Pair programming helps¶
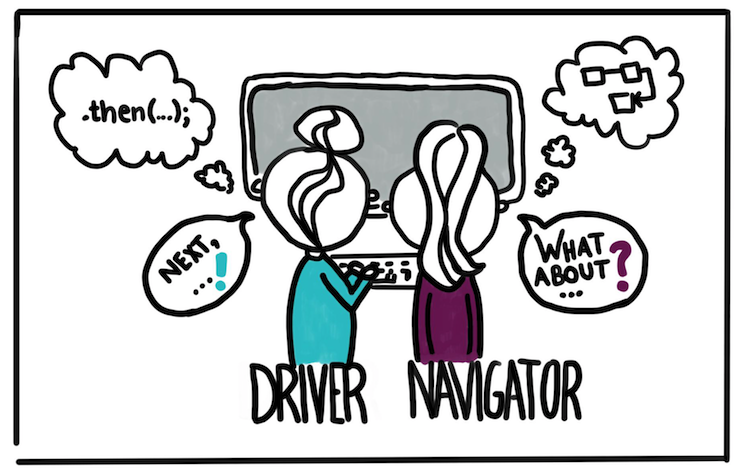
Betty Snyder and I, from the beginning, were a pair. And I believe that the best programs and designs are done by pairs, because you can criticise each other, and find each others errors, and use the best ideas. Jean Bartik, Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (developed in 1945)
...The stickies will help also¶

Computer setup¶
Open up a Jupyter Notebook:¶
- If using a lab computer
- login to OneDrive
- search for "Jupyter Notebook"
- navigate to your OneDrive and create a KD4014 folder
- If using a laptop, follow the setup instructions here: lucydot.github.io/python_novice
Task complete? Explore the course website: lucydot.github.io/python_novice¶
Plain text vs. Jupyter Notebook¶
- Plain text approach:
- write code in a text editor
- save with a
.pyextension - run code using a terminal
- Jupyter notebook approach:
- write code in a jupyter notebook
- run code in a jupyter notebook
- save with a
.ipynbextension
Pairs Task (5 min)¶
Use your Jupyter notebook to...
- write your name in a Markdown cell
- link to your favourite webpage
- calculate 3624357/325
- display a picture, e.g. http://bit.ly/python_cat
Pairs Task (5 min)¶
A. Can you predict what the final value of position is for the code block below?
initial = 'left'
position = initial
initial = 'right'
B. What is a better variable name: m, min or minutes?
Data types¶
| Data type | Python name | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| integer | int | positive or negative whole numbers | -256 |
| float | float | real number | -3.16436 |
| string | str | character string | "20 pence." |
| list | list | a sequence of values | ['frog',2,8] |
+ boolean, dict, tuple, complex, None, set
Pairs Task (5 min)¶
A. Which of the following will print 2.0?
first = 1.0
second = "1"
third = "1.1"
first + float(second)float(second) + float(third)first + int(third)first + int(float(third))int(first) + int(float(third))2.0 * second
B. Write an expression to calculate $s=ut+\frac{1}{2}at^2$
Pairs Task (5 min)¶
Explain in simple terms the order of operations in the following program: when does the addition happen, when does the subtraction happen, when is each function called, etc.
What is the final value of
radiance?
radiance = 1.0
radiance = max(2.1, 2.0 + min(radiance, 1.1 * radiance - 0.5))
Lists¶
| Data type | Python name | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| integer | int | positive or negative whole numbers | -256 |
| float | float | real number | -3.16436 |
| string | str | character string | "20 pence." |
| list | list | a sequence of values | ['frog',2,8] |
Pairs Task (5 mins)¶
- Use slicing to select
oldfromgold - Fill in the blanks so that the program below produces the output at the bottom:
values = ____
values.____(1)
values.____(3)
values.____(5)
print('first time:', values)
values = values[____]
print('second time:', values)
first time: [1, 3, 5]
second time: [3, 5]
For Loops¶

For Loops¶

Pairs Task (5 mins)¶
Reorder and properly indent the lines of code below
so that they print an array with the cumulative sum of data.
The result should be [1, 3, 5, 10].
cumulative += [sum]
for number in data:
cumulative = []
sum += number
sum = 0
print(cumulative)
data = [1,2,2,5]
Conditionals¶
mass = 4.2
if mass > 3:
print(mass, ' is large')
if mass < 2:
print(mass, ' is small')
if 2 <= mass <= 3:
print(mass, ' is just right')
Pairs Task (5 mins)¶
Students with more than 90 should be awarded an A, more than 80 awarded a B and more than 70 awarded a C. What is wrong with the code below? Fix the code so that it works as intended
grade = 95
if grade >= 70:
print("grade is C")
elif grade >= 80:
print("grade is B")
elif grade >= 90:
print("grade is A")
Functions¶
def print_greeting():
print ("Hello!")
Functions¶
def print_personalised_greeting(name):
print ("Hello "+name)
Pairs Task (5 mins)¶
Fill in the blanks to create a function that takes a list of numbers as an argument and returns the first negative value in the list
def first_negative(values):
for v in ____:
if ____:
return ____
Variable Scope¶
pressure = 103.9
def adjust(temperature):
new_temperature = temperature*1.43/pressure
Variable Scope¶
pressure = 103.9
def adjust(temperature):
new_temperature = temperature*1.43/pressure
return new_temperature
⚠️ Programming good practice ⚠️¶
Document your code with docstrings
def calc_bulk_density(mass,volume):
density = mass / volume
return density
⚠️ Programming good practice ⚠️¶
Document your code with docstrings
def calc_bulk_density(mass,volume):
"Return dry bulk density = powder mass / powder volume."
density = mass / volume
return density
What are the other two types of code documentation you can use?
⚠️ Programming good practice ⚠️¶
Test your code
def calc_bulk_density(mass,volume):
"Return dry bulk density = powder mass / powder volume."
assert mass > 0, "mass must be more than zero"
assert volume > 0, "volume must be more than zero"
density = mass / volume
return density
⚠️ Programming good practice ⚠️¶
Focus on readability
- consistency is key
- whitespace (see the PEP8 style guide):
spam(ham[1], {eggs: 2})
spam( ham[ 1 ], { eggs: 2} ) - clear, meaningful variable names (don't just use
x,petc and expect the reader to know what they mean!)
Pairs Task (5 min)¶
- Write a function to calculate the area of a triangle.
- Document your function with a docstring.
- Write an assert statement to test that the function inputs are sensible.
def triangle_area(base,height):
"""returns the area A of a triangle using the formula A=0.5*b*h,
where b is the base and h is the height."""
assert base > 0 and height > 0, "negative lengths are not allowed"
return 0.5*base*height
Task (15 minutes)¶
- Read the Code Quality criteria for the course assessment.
- Read the code below and predict what it does
- Run the code and inspect the output
- Refactor the program to improve the Code Quality. There are six edits (or more!) that can be made. Run the program after each edit to ensure its behavior hasn't changed.
- Compare your rewrite with your neighbor - what did you do the same or different?
import math
import numpy
sping_constant = [3.1,7.2,2.7]
for x,y in enumerate(sping_constant):
mass = 10
k=y
print("The angular frqency is", numpy.sqrt(k/mass))
Python scientific libraries¶
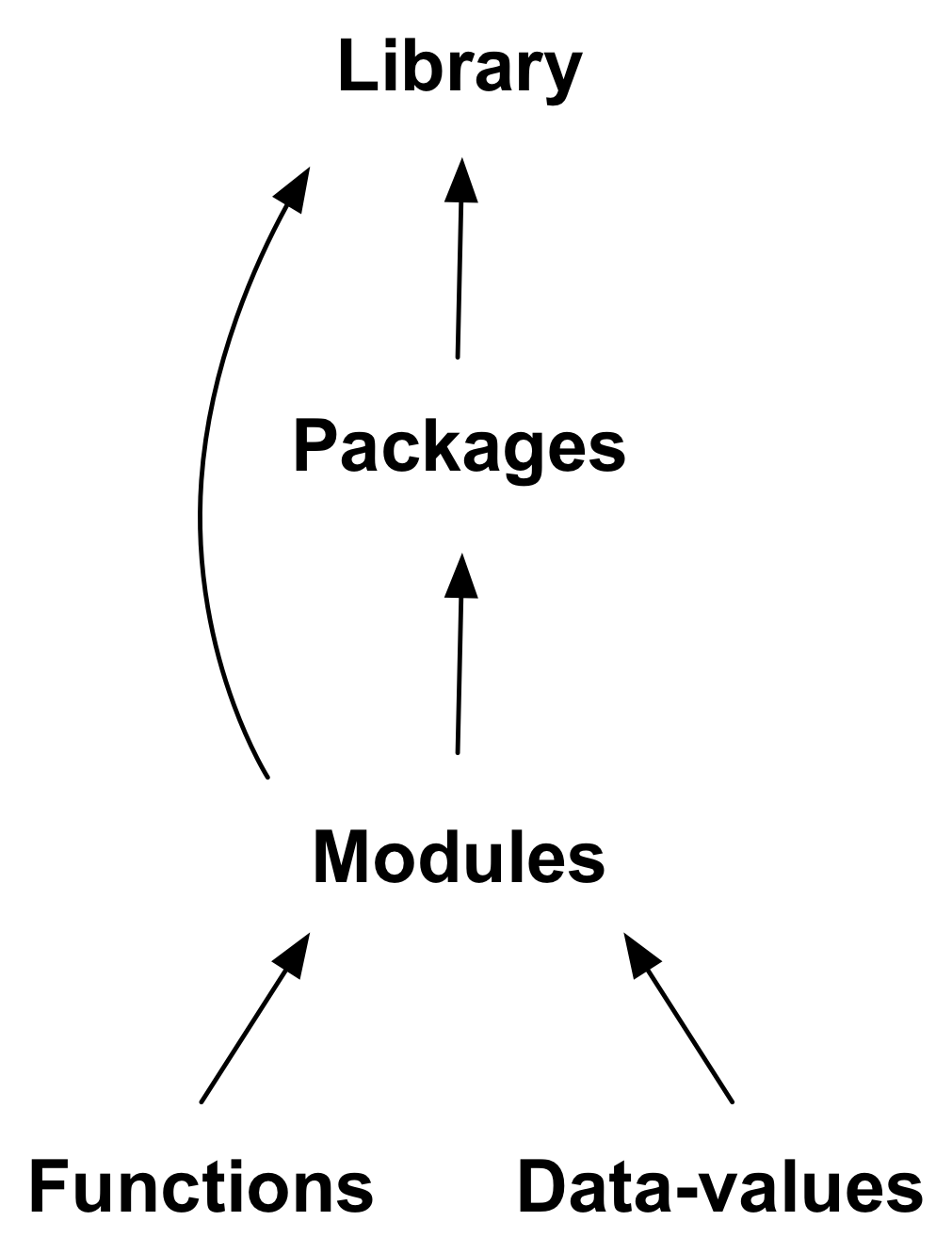
Pairs Task (15 min)¶
You want to select a random character from a string. base = "ATCHAGHRASG"
- which standard library module could help you?
- which function could you select from that module?
- try to write a program that uses that function
Feel free to look online (search for "Python standard library")
⚠️ Programming good practice ⚠️¶
Think about reproducibility
Reproducibility is more complex and difficult than you might think..
One straight-forward thing you can do is print the version number for each package you import using print(packagename.__version__)
Indexing NumPy arrays¶
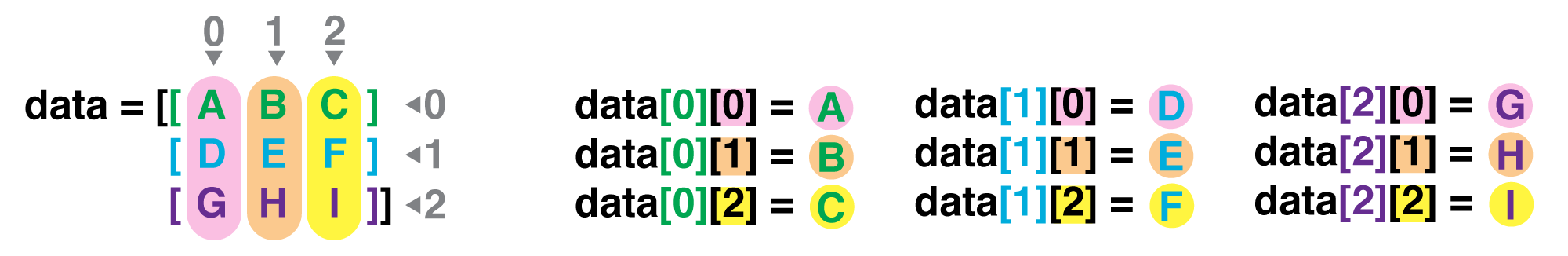
Pairs task (5 min)¶
Crack the code using the following array which has the variable name Cipher:
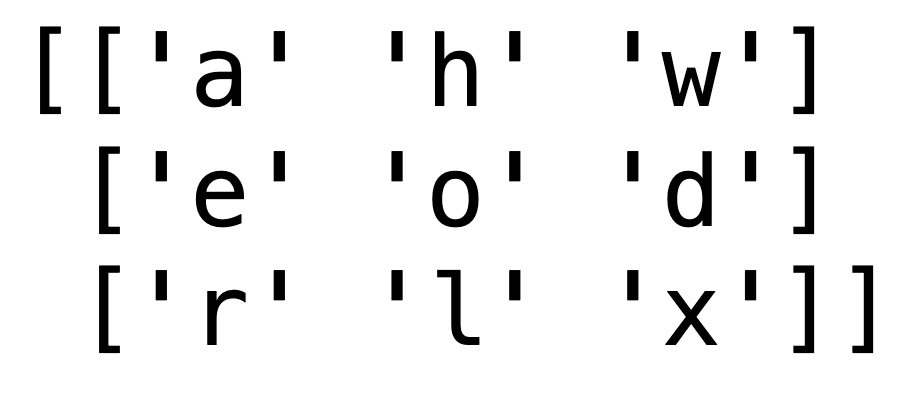
Cipher[0,1],Cipher[1,0],Cipher[2,1]*2,Cipher[1,1]
Cipher[0,2],Cipher[1,1],Cipher[2,0],Cipher[2,1],Cipher[1,2])
Next steps¶
This is just the beginning
You will meet Python again in future years (including KD5081).
You could also...
- Follow up with an online tutorial (e.g. here)
- Adapt what we have done here to create a notebook/script for your own mini-project
- Take part in the Advent of Code